3 steps to lower the risk of hazard trees for electric utilities
Let’s get ahead of the hazard tree problem.
What we’ve always done isn’t enough anymore. Budgets are shrinking, tree health is falling, and the hazards are, well, more hazardous.
Until now, we could just maintain vegetation clearances with routine cycle-trimming. Cut back the trees that overhang now or will soon. Do the occasional emergency work. And keep on going with everyday electric utility vegetation management.
But our forests have changed
Today, we must actively find, prioritize, and mitigate the risk of hazard trees — the tall strike trees outside the right of way (ROW) that are ready to fall into your power lines and transformers.
They’re harder to find than ROW vegetation and more dangerous.
Today, there are more hazard trees than ever.

Thanks to climate change’s increasing temperatures, droughts and pest infestations, vegetation is more stressed than ever. Trees are dying at a much faster rate. Many trees can even die between mid-cycle inspections – as quickly as six months.
Managing the risk of hazard trees comes down to knowing what to do to keep the forest healthy. Access to clear and concise data that helps you see tree health, forest-wide trends. Streamlined prioritization of your responses based on risk helps you reduce risk while you safely manage to a budget.
Lower your hazard tree risk in 3 steps
1. Identify risk
Even when you don’t own or manage the trees outside your rights of way, there are hazard trees there, ready to fall and cause damage and customer interruptions.
Do you know the risks near your ROW?
- Are there multiple tree species, naturally defending against pests and disease?
- Are trees stressed by drought or invasive species?
- Is there any construction that might damage the trees?
- Has soil erosion destabilized any trees? Which ones?
- Have storms, floods, or wildfires damaged trees or ecosystems?
With awareness of these problems, you can address them for trees you own and with the stewards of the trees you don’t own.
2. Monitor risk
Some risks can’t be avoided, and you have to keep an eye on them. Even if that means watching millions or billions of trees.
Drought has long-term impacts on tree health. You need to know where moisture levels have dropped and stressed tree health.
On the other hand, runoff from storm-swollen rivers is equally damaging. Understand which parts of your forest are suffering from too much moisture.

Watch for symptoms that point to underlying problems:
- Are chlorophyll levels low?
- Has soil eroded anywhere?
- Has growth slowed over time?
- Has tree mortality increased?
Manual and cycle inspections make these signs of tree health nearly impossible to spot because of the limitations of human inspections. It’s so expensive to send out arborists to personally evaluate trees.
Luckily, there’s technology available to help you get a get a view of your outside-the-ROW hazards. Satellite and AI technology actually lets you assess tree heath at scale. It also lets you efficiently focus inspections where they are most needed.
By getting the data you need to watch emerging problems, you can resolve them more quickly and avoid the devastation that may follow — and the effect it has on your budgets and reliability.
3. Remove risk
Despite all the prevention and monitoring, some of your trees will be clear and present dangers. You need to act, but where do you start?
Detect hazard trees and prioritize their removal by assessing the potential impact to your lines, your communities, your workers, and your budget.
- Which hazard trees might fall on a distribution line?
- Which trees are near community centers or houses?
- What’s the right equipment for your workforce to use, given a tree’s location and surrounding terrain?
- Which problem trees can you remove with workers and equipment that are already nearby for scheduled trimming?
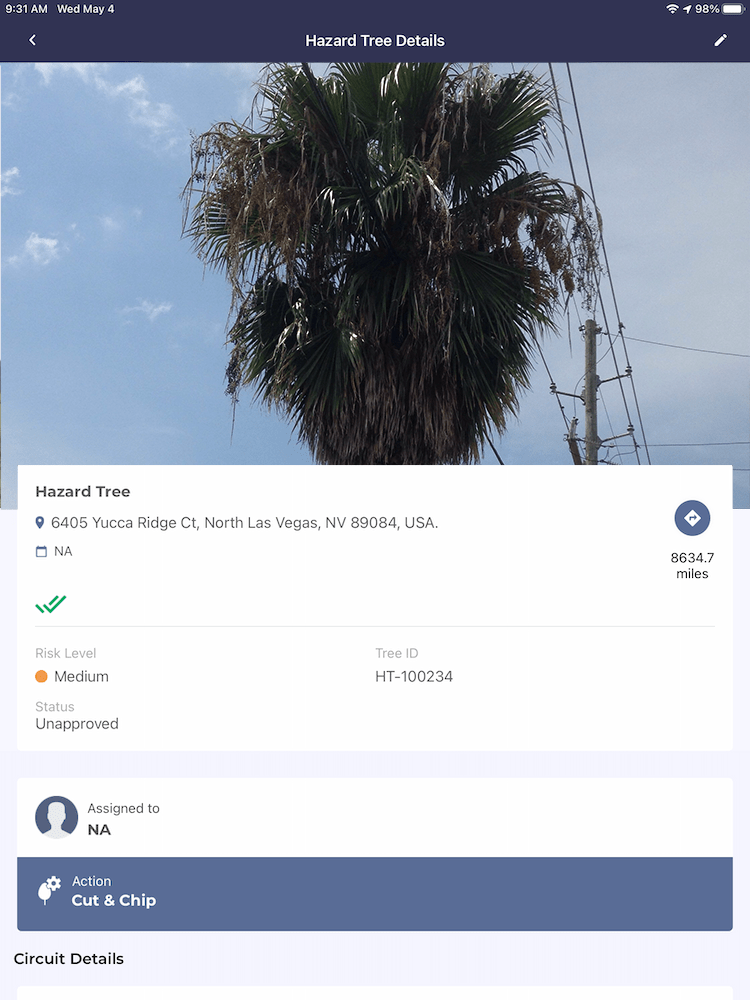
Quick but thoughtful analysis — aided by today’s intelligent vegetation management system — helps you minimize disruptions to your customers and to your budgets.
Get the data to see and lower your risk
Some of these insights used to be hard to get across large territories. But today, satellite-powered vegetation management gives you a near-real-time 3-D scan of the tree health near your entire network.
That helps you to understand and predict changes in your forests:
- Past and future tree mortality.
- Tree stressors.
- Unhealthy trees.
- Dead trees with strike potential.
- Nearby construction.
- Moisture content.
- Soil conditions.
- Chlorophyl content.

You get important insights to get the right person to the right tree at the right time:
- Health risks in any circuit at any time.
- Early detection of tree health issues.
- Prioritization of hazard trees.
- Potential impact of fall-ins causing outages or sparking wildfires.
- Immediate attention to the most dangerous trees.
- Cost-effective grouping of vegetation management work.
- What equipment each site needs for safe mitigation work.
- Site requirements like traffic control, access and local permissions.
- Historical views of erratic seasonal changes that may mean the forest is unhealthy.
This rapid data capture of satellite-based vegetation monitoring can give you the insight to find your risks, watch them closely, and then remove them safely if it comes to that.
Want to see what data-driven risk management for hazard trees looks like for your utility? Talk with a specialist today.
