Remote sensing 101: From Sputnik to hyperspectral and why it matters for core industries
What is remote sensing?
Remote sensing, or remote monitoring, is observing an object or area, and then acquiring data, without actually coming into contact with the object. Remote sensing is typically used when thinking about earth observation through satellites, but it is also used with aerial photography and scanning.
Unlike on-site observation, remote sensing is completely hands off — able to observe and analyze a site without ever stepping foot on it.
Remote sensing really became popular in 1957 with the launch of Sputnik 1, which could complete an orbit around earth in 96 minutes and was the first satellite able to transmit signals back to earth.
This new capability kicked off the remote sensing era. Traditionally this has been used for governments, military, and educational purposes, but with over 1,000 new satellites launched each year, it’s now being used for core industries like utilities, transportation, and even for sustainability monitoring.
How does remote sensing work?
Remote sensing works via an object, usually either a satellite or aircraft, that flies over an area and captures imagery. That imagery is then analyzed and used to make a variety of business decisions.
Since the Sputnik satellite, remote sensing has evolved from a single optical sensor to multispectral, and even hyperspectral imaging.
Optical sensors work much like a standard camera. They take a picture of an area, and depending on the resolution, it’s like looking at an area with the human eye.
However, new sensors are constantly being added to satellites to capture more and more waves or bands of light. The more bands that can be captured, the more detail you have for analysis.
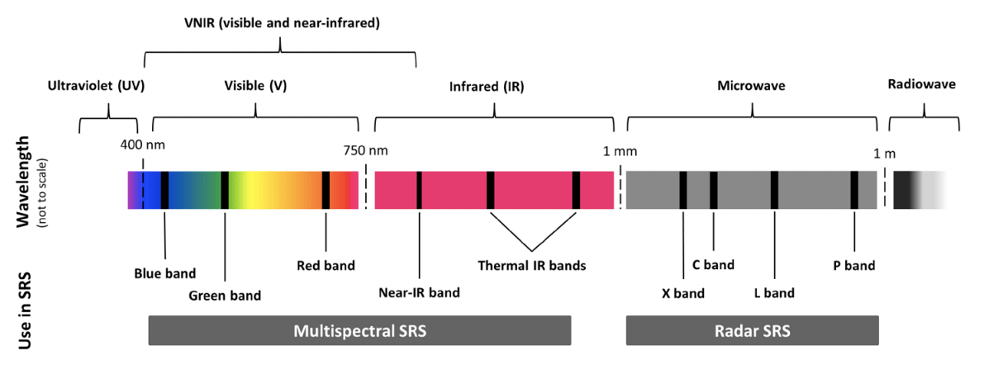
As a reference, multispectral imagery uses about 10 bands of light. This amount is in contrast to the 3 visible bands the human eye can see. Hyperspectral uses hundreds of bands.
For example, hyperspectral imagery can detect nutrients within soil from space, or the amount of chlorophyll in trees.
There are also thermal satellites for heat sensing, as well as synthetic aperture radar (SAR) satellites that can see at night and pierce through cloud cover, which has become especially useful in disaster management situations.
Why is remote sensing important for core industries?
One of the main benefits of remote sensing is the scale it provides. So, naturally, industries with geographically distributed assets are a perfect fit.
Electric utilities have thousands of miles of rights of way (ROWs) and overhead power lines to cover.
Oil and gas utilities have pipeline infrastructure throughout the world that must be monitored for encroachment or erosion.
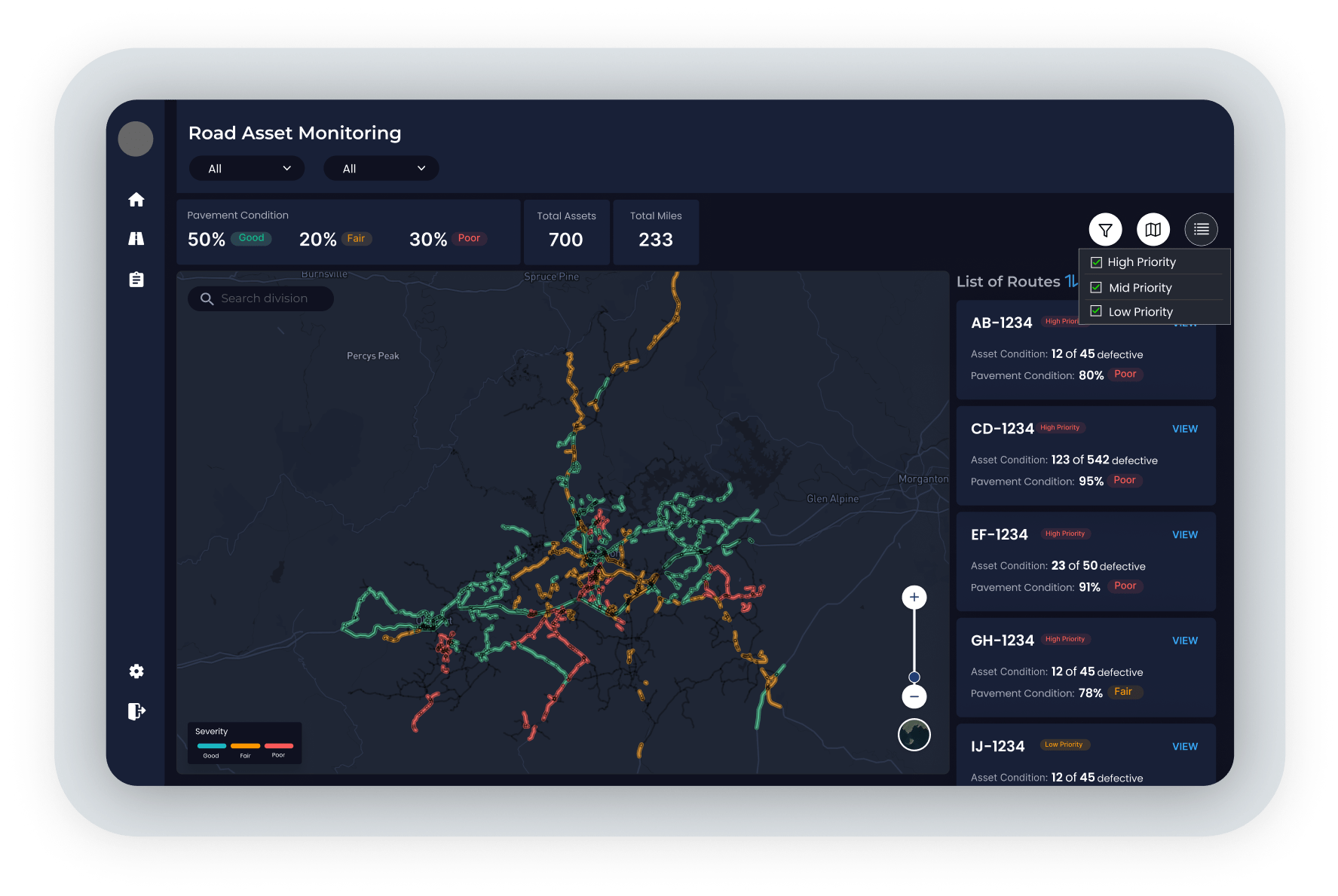
Roadways, railways, and mines must be continuously monitored for safety and regulatory concerns.
Not to mention the land holdings that core industries tend to have spread throughout a city, state, or country that need to be monitored and assessed for sustainability reporting.
The nature of geographically distributed assets makes them extremely hard to manage manually.
It involves a lot of boots on the ground, which leads to worker safety concerns and human errors in reporting. Frankly, manual administration isn’t an efficient use of budget and resources.
With remote sensing, namely satellites, these sprawling networks can be assessed, analyzed, and managed with the press of a button. Prioritizing areas based on risk or criticality allows teams to be precise with on-the-ground efforts.
Remote sensing has also opened up the ability to truly manage sustainability at scale, with satellites being able to measure biodiversity, methane and other GHG emissions, carbon sequestration, and more.
What are the benefits of remote sensing?
Remote sensing offers a host of benefits depending on your use case, but there are some general themes that remote sensing brings to any operation. Here are 6 of the top benefits of remote sensing.
1. Scale
The #1 benefit of remote sensing is scale.
Let’s say a utility has 10,000 miles of overhead lines to inspect. A team could do 30-50 miles per day, if they are truly getting out of the trucks, climbing poles, measuring clearances, and doing a proper in-depth risk assessment.
With satellite-powered vegetation management, all 10,000 miles can be scanned, analyzed, categorized, and prioritized by criticality almost instantly.
Or a company that wants to start measuring and reporting on sustainability metrics for their investors. It has 2,500 land sites spread across the country. 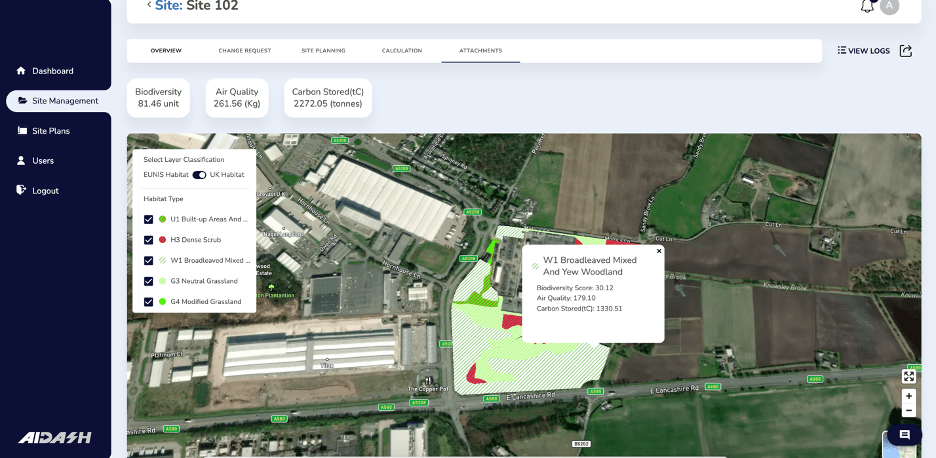
Sending teams of ecologists or other environmental consultants to each site could take years and isn’t realistic to fit in the budget. But with remote sensing satellites and AI, you can assess all those land assets at once, measuring biodiversity, carbon sequestration, emissions – and even get a nice report at the end, along with recommendations for improvement.
2. Efficiency
Manually driving to inspect thousands of miles of distributed assets and their ROWs isn’t an efficient process.
In vegetation management, there might be 1,000 trees in a given area that a pre-inspector is sent to. That pre-inspector is going to inspect the first 100 trees they see.
What if you could point them exactly where the top 100 riskiest trees are from the start? Or for pipeline integrity, what if they knew exactly where areas of encroachment concern were, instead of driving miles hoping to spot something?
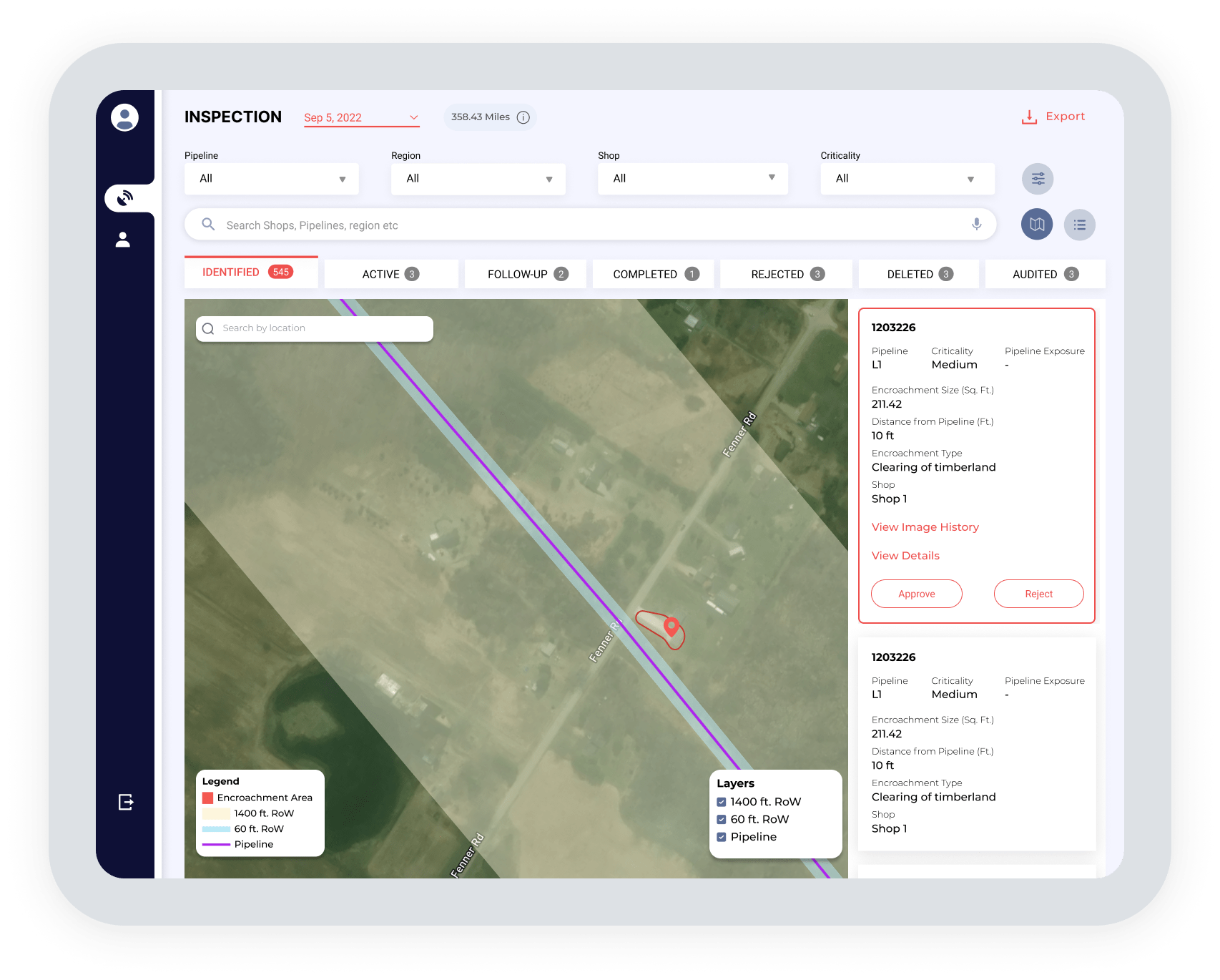
Remote sensing isn’t going to replace boots on the ground. Experts in the field will always be needed. Remote sensing is just helping those experts use their time efficiently and be very precise with their inspections.
3. Automation
This may not be a benefit for all remote sensing techniques, but by combining satellites and AI (like AiDASH does) a new layer of automation gets added.
The system can automatically create work plans, within your budget, given the risk-based recommendations, and then send them to a manager for approval. This capability can cut down countless hours of assessing, planning, creating work plans, and coordinating with contractors.
4. Resiliency
The goal of remote sensing is to spot risks and areas of improvement at scale. Getting a view of your entire network, and drilling down into risk areas, or grid-hardening opportunities, can provide a massive lift to overall resiliency and reliability.
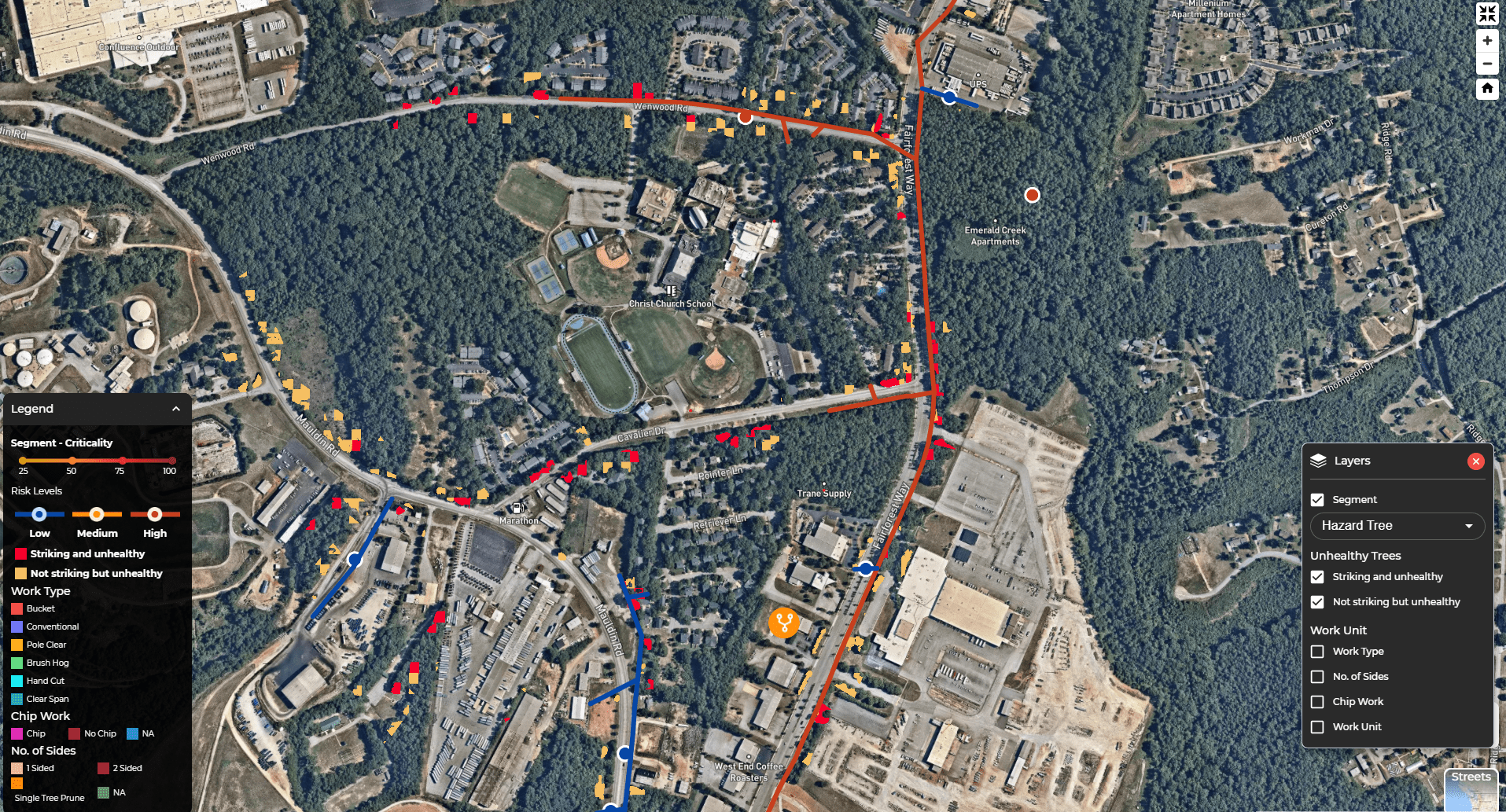
Not just that, but new developments also allow for satellites to monitor tree health, allowing you to spot potential hazards at the earliest stages possible and mitigate that risk before a fall-in outage or wildfire occurs.
5. Compliance
Core industries are highly regulated, that’s no secret.
From FAC-003-4, to the 2019 PHMSA bulletin, to new biodiversity regulations — core industries all have a regulatory body to work with and regulations to maintain.
This isn’t always an easy or straightforward task. Remote sensing provides real data to bring to regulators to prove that you’re actively working on a plan and can even help to decrease your liability should a disaster occur.
Think of it almost like a paper trail. You run analysis spotting areas of concern or high risk. The system flags these and gives recommendations to provide the best results in your budget. Then you can do a post-work audit after the fact using satellite imagery to ensure the right work was done in the right area.
Taking that data-driven plan to regulator is a massive asset in your corner and may even help you make the case for more funding.
6. Seeing beyond human eyes
Nothing can replace boots-on-the-ground inspections, but there are some advantages remote sensing with satellites can bring to the party:
- Multi- and hyperspectral imagery opens the window to new insights: things like moisture content, chlorophyll content, erosion, soil nutrients — even detecting early signs of tree health decline or pest infestation. Those are things humans simply can’t see, at least not before significant decline.
- Remote sensing lets you see physical changes over incredibly large areas at once.
- Satellites give you the ability to time travel: With 50+ years of historical imagery to draw from, you can see change over time in vegetation or geography, and even predict into the future what changes are likely to come next. That kind of insight simply can’t come from manual inspection alone.
It’s clear that for core industries remote sensing — namely satellites and AI — are the future. The technology is rapidly advancing, and new use cases are unlocked every day.
Remote sensing tools are truly giving organizations the ability to achieve resiliency, efficiency, and sustainability in a way that simply wasn’t possible before.
One of our customers put it this way “The ability to open my computer and to know everything all at once is a game changer. I can have a bird’s eye view of my entire network to see exactly what needs to be done to achieve my goals. It’s truly a powerful technology.”
Want to see how remote sensing solutions like satellites and AI can help you become more resilient, efficient, and sustainable? Get in touch today to learn more.
